This report represents a security audit performed by Hacker Vaccine. It contains confidential information about the state of your network. Access to this information by unauthorized personnel may allow them to compromise your network.
|
Site Name |
Start Time |
End Time |
Total Time |
Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Faux Systems |
June 26, 2012 13:01, CDT |
June 26, 2012 13:45, CDT |
44 minutes |
Success |
There is not enough historical data to display overall asset trend.
The audit was performed on one system which was found to be active and was scanned.
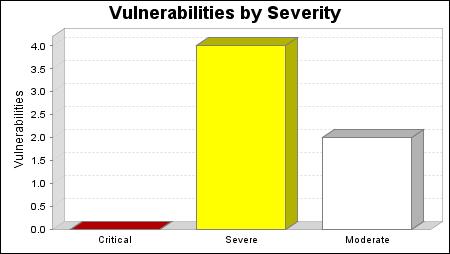 |
There were 6 vulnerabilities found during this scan. No critical vulnerabilities were found. Critical vulnerabilities require immediate attention. They are relatively easy for attackers to exploit and may provide them with full control of the affected systems. 4 vulnerabilities were severe. Severe vulnerabilities are often harder to exploit and may not provide the same access to affected systems. There were 2 moderate vulnerabilities discovered. These often provide information to attackers that may assist them in mounting subsequent attacks on your network. These should also be fixed in a timely manner, but are not as urgent as the other vulnerabilities.
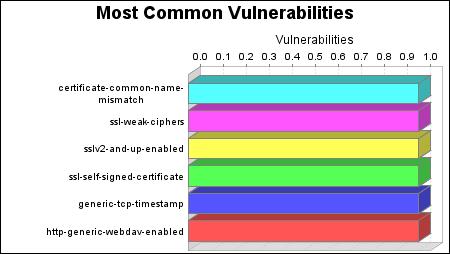 |
There were 1 occurrences of the certificate-common-name-mismatch, ssl-weak-ciphers, sslv2-and-up-enabled, ssl-self-signed-certificate, generic-tcp-timestamp and http-generic-webdav-enabled vulnerabilities, making them the most common vulnerabilities.
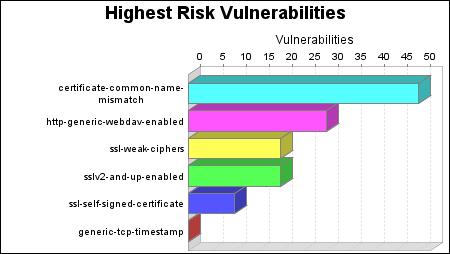 |
The certificate-common-name-mismatch vulnerability poses the highest risk to the organization with a risk score of 50. Vulnerability risk scores are calculated by looking at the likelihood of attack and impact, based upon CVSS metrics. The impact and likelihood are then multiplied by the number of instances of the vulnerability to come up with the final risk score.
One operating system was identified during this scan.
There were 3 services found to be running during this scan.
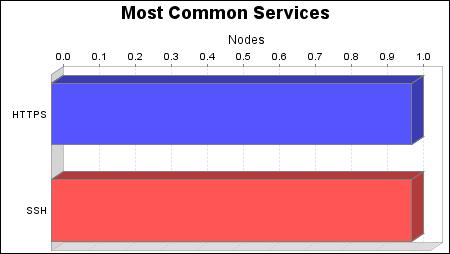 |
The HTTPS and SSH services were found on 1 systems, making them the most common services.